Install Crucible for C Programs
This post is based on text from Crucible repository.
Crucible is a language-agnostic library for performing forward symbolic execution of imperative programs. It provides a collection of data-structures and APIs for expressing programs as control-flow graphs. Programs expressed as CFGs in this way can be automatically explored by the symbolic execution engine. In addition, new data types and operations can be added to the symbolic simulator by implementing fresh primitives directly in Haskell. Check out the GitHub at https://github.com/GaloisInc/crucible
For the next steps, we adopted a Linux docker container, aiming to keep a pattern for our commands.
-
Install docker, checking out this LINK
-
Create our container:
foo@bar:~$ docker run -it --name crucible ubuntu:18.04 /bin/bash
Unable to find image "ubuntu:18.04" locally
18.04: Pulling from library/ubuntu
423ae2b273f4: Pull complete
de83a2304fa1: Pull complete
f9a83bce3af0: Pull complete
b6b53be908de: Pull complete
...
root@a3cbc72a4874:/#
- Install Crucible and fetching the dependencies. In this step, we’ll install tools, such as ghc (Haskell compiler) v8.6.5, Boost library (libboost-all-dev), Number Theory Library (libntl-dev) development files, and GNU Linear Programming Kit. Let’s go to the commands:
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# apt update
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# apt install software-properties-common -y
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# add-apt-repository ppa:hvr/ghc -y
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# apt update
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# apt install ghc-8.6.5 -y
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# ln -s /opt/ghc/bin/ghc-8.6.5 /usr/bin/ghc
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# apt install cabal-install-3.0 -y
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# ln -s /opt/cabal/bin/cabal-3.0 /bin/cabal
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# apt install git -y
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# apt install libboost-all-dev -y
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# apt install libntl-dev -y
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# apt install libglpk-dev -y
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# apt install libncurses5-dev -y
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# cd home
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# git clone https://github.com/GaloisInc/crucible.git
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# cd crucible
-
From the Crucible repository, we’ll get the following Haskell packages: crucible, crucible-llvm, crucible-saw, crucible-syntax, and crux. Additionally, the crux-llvm library/executable package that is a standalone frontend for executing C and C++ programs in the crucible symbolic simulator. The front-end invokes clang to produce LLVM bitcode and runs the resulting programs using the crucible-llvm language frontend.
-
Let’s build the Crucible packages, starting to fetch all the latest git versions of immediate dependencies of libraries in this repository:
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# ./scripts/build-sandbox.sh
...
Submodule 'abc-build' (https://github.com/GaloisInc/abc.git) registered for path 'dependencies/what4/dependencies/abcBridge/abc-build'
Cloning into '/home/crucible/dependencies/what4/dependencies/abcBridge/abc-build'...
Submodule path 'dependencies/what4/dependencies/abcBridge/abc-build': checked out 'c78ee31186ab4da49f348f1262c27c0a048bba82'
Submodule path 'dependencies/what4/dependencies/aig': checked out 'b59077c065b659e985ee25966809dd448a0d595a'
Submodule path 'dependencies/what4/dependencies/blt': checked out 'd0c8d9d14fe1bb43045ca04d6961a6290af637b7'
Submodule path 'dependencies/cryptol-verifier': checked out 'f33f4f234da9f48664f61bd9492b09259c78b60f'
Submodule path 'dependencies/jvm-parser': checked out '5368a84117dc28e0002003e8d8a491dd8756b421'
- Update the Haskell packages and build the Crucible packages.
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# cabal update
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# cabal new-configure
...
crux-llvm-0.3.2 (test:crux-llvm-test) (first run)
crux-llvm-0.3.2 (exe:crux-llvm-svcomp) (first run)
crux-llvm-0.3.2 (exe:crux-llvm) (first run)
crucible-mc-0.1.0.0 (exe:crucible-mc) (first run)
cryptol-verifier-0.1 (exe:css) (first run)
cryptol-verifier-0.1 (test:cryptol-verifier-tc-test) (first run)
crucible-server-0.1 (first run)
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# cabal new-build crucible
...
[50 of 50] Compiling Lang.Crucible.Vector ( src/Lang/Crucible/Vector.hs, /home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crucible-0.5/build/Lang/Crucible/Vector.o )
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# cabal new-build crucible-llvm
...
[44 of 44] Compiling Lang.Crucible.LLVM.Ctors ( src/Lang/Crucible/LLVM/Ctors.hs, /home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crucible-llvm-0.3/build/Lang/Crucible/LLVM/Ctors.o )
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# cabal new-build crucible-saw
...
[1 of 1] Compiling Lang.Crucible.Backend.SAWCore ( src/Lang/Crucible/Backend/SAWCore.hs, /home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crucible-saw-0.1/build/Lang/Crucible/Backend/SAWCore.o )
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# cabal new-build crucible-syntax
...
[1 of 1] Compiling Main ( crucible-syntax/Main.hs, /home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crucible-syntax-0.1/x/crucibler/build/crucibler/crucibler-tmp/Main.o )
Linking /home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crucible-syntax-0.1/x/crucibler/build/crucibler/crucibler ...
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# cabal new-build crux
...
[18 of 18] Compiling Crux ( src/Crux.hs, /home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crux-0.1/build/Crux.o )
root@a3cbc72a4874:/# cabal new-build crux-llvm
...
[1 of 1] Compiling Main ( svcomp/Main.hs, /home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crux-llvm-0.3.2/x/crux-llvm-svcomp/build/crux-llvm-svcomp/crux-llvm-svcomp-tmp/Main.o )
Linking /home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crux-llvm-0.3.2/x/crux-llvm/build/crux-llvm/crux-llvm ...
Linking /home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crux-llvm-0.3.2/x/crux-llvm-svcomp/build/crux-llvm-svcomp/crux-llvm-svcomp ...
It’s done.
Install LLVM v8
- The LLVM tool, e.g., Clang-8 allows the Crucible to execute the C code verification.
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# apt install -y build-essential subversion cmake ninja-build python-minimal wget
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# echo "deb http://apt.llvm.org/xenial/ llvm-toolchain-xenial-8 main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# echo "deb-src http://apt.llvm.org/xenial/ llvm-toolchain-xenial-8 main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# wget -O - https://apt.llvm.org/llvm-snapshot.gpg.key|apt-key add -
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# apt update
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# apt install aptitude -y
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# aptitude install libllvm-8-ocaml-dev libllvm8 llvm-8 llvm-8-dev llvm-8-doc llvm-8-examples llvm-8-runtime -y
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# aptitude install clang-8 clang-tools-8 clang-8-doc libclang-common-8-dev libclang-8-dev libclang1-8 clang-format-8 python-clang-8 -y
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# ln -s /usr/bin/clang-8 /usr/bin/clang
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# ln -s /usr/bin/opt-8 /usr/bin/opt
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# ln -s /usr/bin/llvm-link-8 /usr/bin/llvm-link
Install a Solver
In this case, we’ll install Yices as an SMT solver. Further details at https://yices.csl.sri.com/
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# add-apt-repository ppa:sri-csl/formal-methods -y
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# apt-get update
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# apt-get install yices2 -y
Testing Crucible LLVM
In this step we’ll adopt the following code using SV-COMP rules to check a given code:
- Setting up:
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# cd dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crux-llvm-0.3.2/x/crux-llvm/build/crux-llvm/ root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# cp -r /home/crucible/crux-llvm/c-src .
// test.c code
#include <stdint.h>
#include <crucible.h>
int8_t f(int8_t x) {
return x + 1;
}
int main() {
int8_t x = crucible_int8_t("x");
assuming(x < 100);
check(f(x) < 100);
return 0;
}
- Running:
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# ./crux-llvm test.c -x ... [CLANG] clang "-c" "-g" "-emit-llvm" "-O1" "-I" "." "-I" "c-src/includes" "-o" "test.bc" "test.c" [Crux] Simulating function "main" [Crux] Attempting to prove verification conditions. [Crux] Goal status: [Crux] Total: 1 [Crux] Proved: 0 [Crux] Disproved: 1 [Crux] Incomplete: 0 [Crux] Unknown: 0 [Crux] Overall status: Invalid. - NOTE: The crucible.h API allows for better explanations by a) allowing user-specified names for non-deterministic variables, and b) ensuring that the conditions used in assertions are directly available and not obscured by a conditional wrapper around an error function. It’s possible you need to fix the header path, e.g., replace
by "crucible.h".
Testing Crucible LLVM using SV-COMP definitions
- The following example.c code has the __VERIFIER_ERROR() function the points an error location in the code. This way, the goal of the code verification is found values to reach code location.
extern void __VERIFIER_error() __attribute__((__noreturn__));
extern int __VERIFIER_nondet_int(void);
int main(){
int a = __VERIFIER_nondet_int();
int b = __VERIFIER_nondet_int();
if( (a+b) > 42 ){
__VERIFIER_error();
}
return 0;
}
- Running:
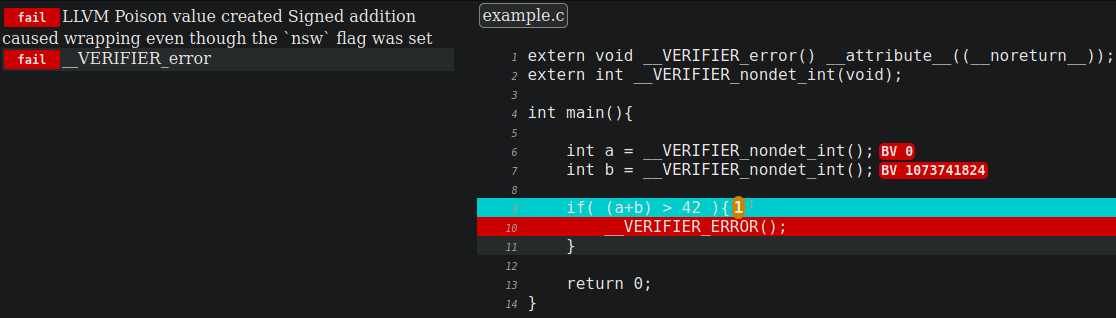
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# ./crux-llvm example.c -x [CLANG] clang "-c" "-g" "-emit-llvm" "-O1" "-I" "." "-I" "c-src/includes" "-o" "example.bc" "example.c" [Crux] Simulating function "main" [Crux] Attempting to prove verification conditions. [Crux] Goal status: [Crux] Total: 2 [Crux] Proved: 0 [Crux] Disproved: 2 [Crux] Incomplete: 0 [Crux] Unknown: 0 [Crux] Overall status: Invalid. - NOTE: In this code verification Crucible set to verification condition: overflow, and reach check. Now let’s check the report:
root@a3cbc72a4874:/home/crucible# cat results/example/report.js var goals = [{"status": "fail","counter-example": [ {"name": "X","loc": {"file": "/home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crux-llvm-0.3.2/x/crux-llvm/build/crux-llvm/example.c","line": "6","col": "13"},"val": "BV 2147483648","bits": "32"} , {"name": "X","loc": {"file": "/home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crux-llvm-0.3.2/x/crux-llvm/build/crux-llvm/example.c","line": "7","col": "13"},"val": "BV 2147483648","bits": "32"} ] ,"goal": "LLVM Poison value created\nSigned addition caused wrapping even though the `nsw` flag was set","location": {"file": "/home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crux-llvm-0.3.2/x/crux-llvm/build/crux-llvm/example.c","line": "9","col": "11"},"assumptions": [],"trivial": false,"path": []},{"status": "fail","counter-example": [ {"name": "X","loc": {"file": "/home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crux-llvm-0.3.2/x/crux-llvm/build/crux-llvm/example.c","line": "6","col": "13"},"val": "BV 0","bits": "32"} , {"name": "X","loc": {"file": "/home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crux-llvm-0.3.2/x/crux-llvm/build/crux-llvm/example.c","line": "7","col": "13"},"val": "BV 1073741824","bits": "32"} ] ,"goal": "__VERIFIER_error","location": {"file": "/home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crux-llvm-0.3.2/x/crux-llvm/build/crux-llvm/example.c","line": "10","col": "9"},"assumptions": [{"loc": {"file": "/home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crux-llvm-0.3.2/x/crux-llvm/build/crux-llvm/example.c","line": "9","col": "9"}}],"trivial": false,"path": [{"loop": [1],"loc": {"file": "/home/crucible/dist-newstyle/build/x86_64-linux/ghc-8.6.5/crux-llvm-0.3.2/x/crux-llvm/build/crux-llvm/example.c","line": "9","col": "9"}}]}] - Let’s focus on the values generated to reach the line:
- “line”: “6”,”col”: “13”},”val”: “BV 0”
- “line”: “7”,”col”: “13”},”val”: “BV 1073741824”
Aiming to get a better way to visualize you should see the files at path results/example/
- Goal 1 to check, possible overflow
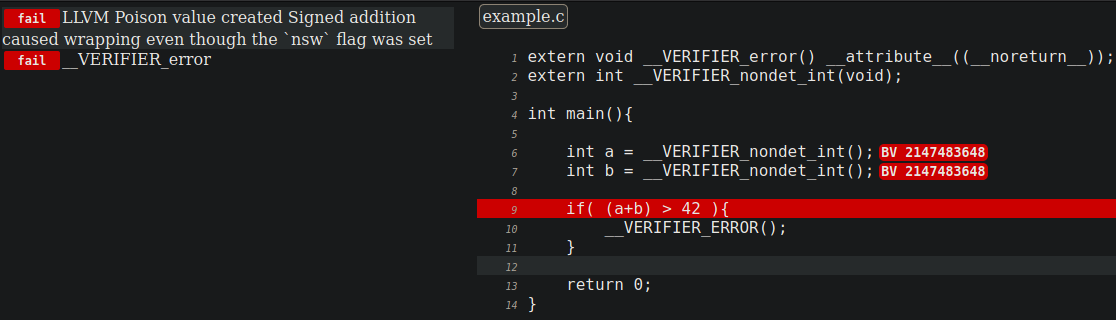
- Goal 2 to check, reach check